Moderne today revealed a pair of alliances with Diffblue and Azul Systems that promise to accelerate application modernization initiatives.
As a provider of a platform that leverages an open-source OpenRewrite Lossless Semantic Trees (LSTs) project to create structured representations of complex codebases developed by Moderne, the alliances with Diffblue and Azul provide deeper integrations with unit testing tools and a Java code analytics platform, respectively.
Moderne CEO Jonathan Schneider said, for example, DevOps teams will be able to more easily test refactored code using Diffblue Cover testing tools that employ machine learning algorithms and reinforcement learning to automatically generate unit tests.
In a similar fashion, Azul, a provider of a Java virtual machine (JVM) platform, has developed Code Inventory, a module within the Azul Intelligence Cloud platform that surfaces insights into runtime environments. That integration will make it simpler for DevOps teams to identify, for example, dead code to reduce the overall footprint of a Java application, said Schneider.
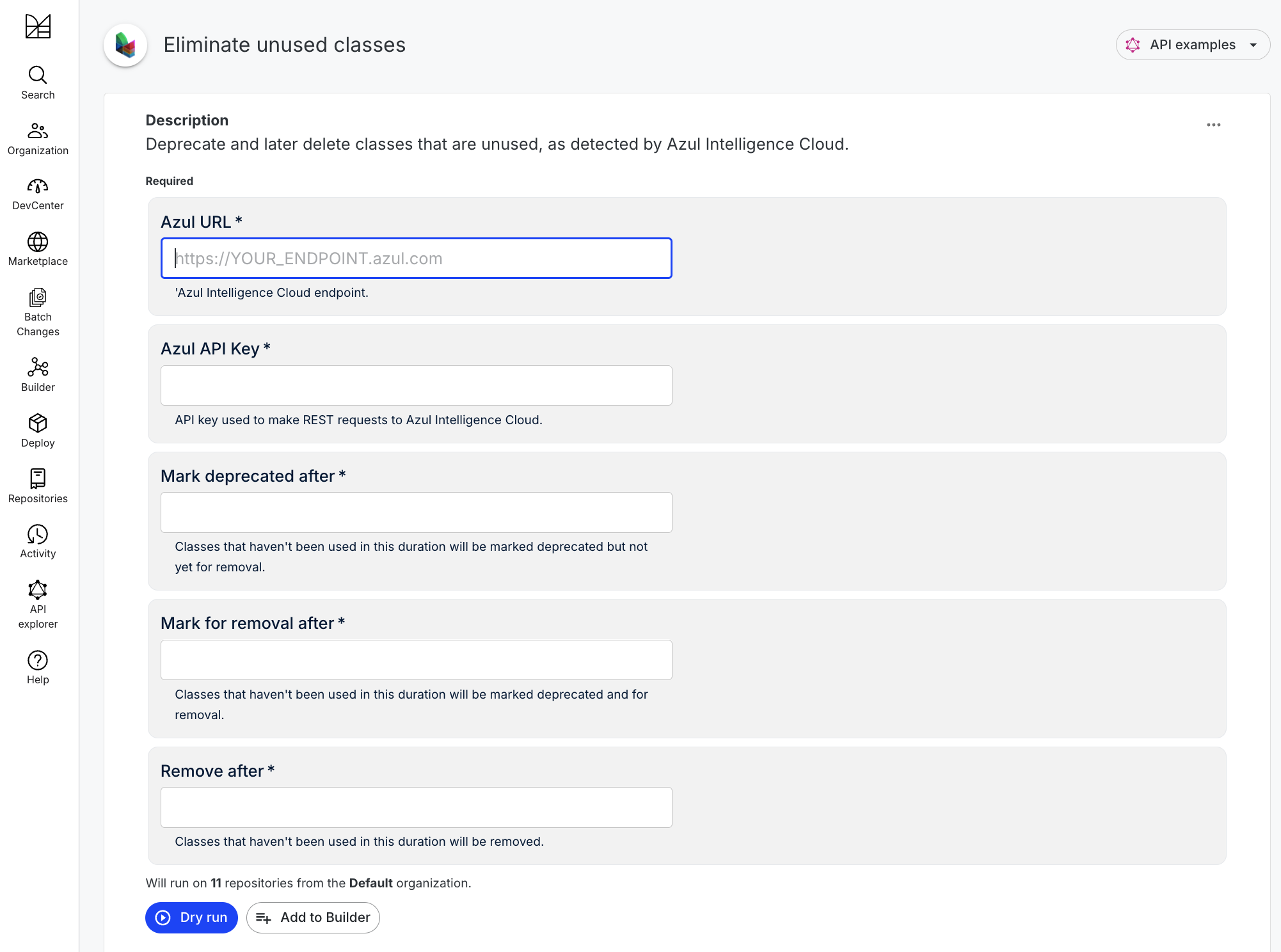
Moderne uses the OpenRewrite LST platform to provide DevOps teams with a set of extensible recipes for refactoring legacy applications that can be used to programmatically modernize code bases. Those recipes are now being extended to include offerings from third-party vendors such as Diffblue and Azul to streamline application modernization workflows, said Schneider.
Additionally, Moderne has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) agent, dubbed Moddy, that automates tasks such as determining where payment processing is occurring within an application spanning multiple code bases. That capability is critical because it enables DevOps teams to leverage recipes to update code spanning multiple applications, rather than having to manually address each instance of that code one application at a time, noted Scheider.
It’s not clear how many application modernization initiatives organizations might either have already launched or are being considered, but during uncertain economic times, there is typically much greater sensitivity to the total cost of IT. One of the primary goals of such initiatives is to enable organizations to either move an application to a platform that is less expensive to run or, less ambitiously, simply make it consume fewer infrastructure resources.
Historically, the challenge has been that the level of manual effort required to achieve those goals can take months, sometimes even years, to complete. The OpenRewrite LST platform provides a more programmatic alternative that can be integrated with various generative AI tools and platforms to reduce the overall amount of manual effort that would otherwise be required.
The level of complexity involved with modernizing applications will, of course, vary widely. Moving an application from one virtual machine to another or updating it to run the latest version of Java is not nearly as complex an endeavor as trying to convert COBOL code into another programming language so that an application can run on another platform. Regardless of the scope of the project, however, as the amount of manual effort required continues to decline, the number of these initiatives that organizations might be willing to undertake should correspondingly increase.





